Google Tag Manager, often called GTM, has become one of the most important tools for modern marketers, analysts, and website owners. If you have ever needed to add tracking code to your website, such as Google Analytics for traffic insights, Google Ads conversion tracking, Facebook Pixel, LinkedIn Insight Tag, or any other marketing script, you already know the challenge. You usually need to wait for a developer or web operations team to deploy the changes. Google Tag Manager comes for the resuce. In this article I will show you what is Google Tag Manager, how to use it to setup your marketing scripts with ease, and more.
Why Google Tag Manager?
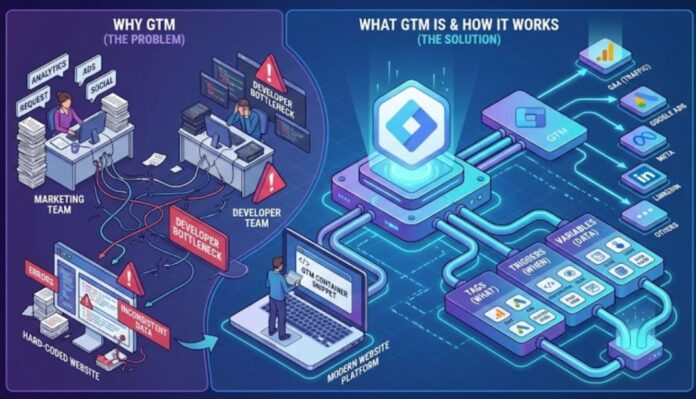
Years ago, whenever a marketing or analytics team wanted to implement a new tracking script or event, they had to send that code to the web development team.
Want to add Google Analytics? Send them the script.
Need to track purchases for Google Ads? Another script.
Want to install a Facebook Pixel? Yet another script.
Since development teams typically work in release cycles of two to four weeks, even simple marketing changes could get delayed. Tracking became slow, inconsistent, and difficult to maintain. Old scripts stayed in place, new ones overlapped, and audits were complicated.
This led to the rise of Tag Management Systems, often called TMS. These systems were designed to centralize tracking and give marketers more control. Google Tag Manager quickly became the most popular among them due to being free, flexible, and easy for non-developers to adopt.
What Is Google Tag Manager?
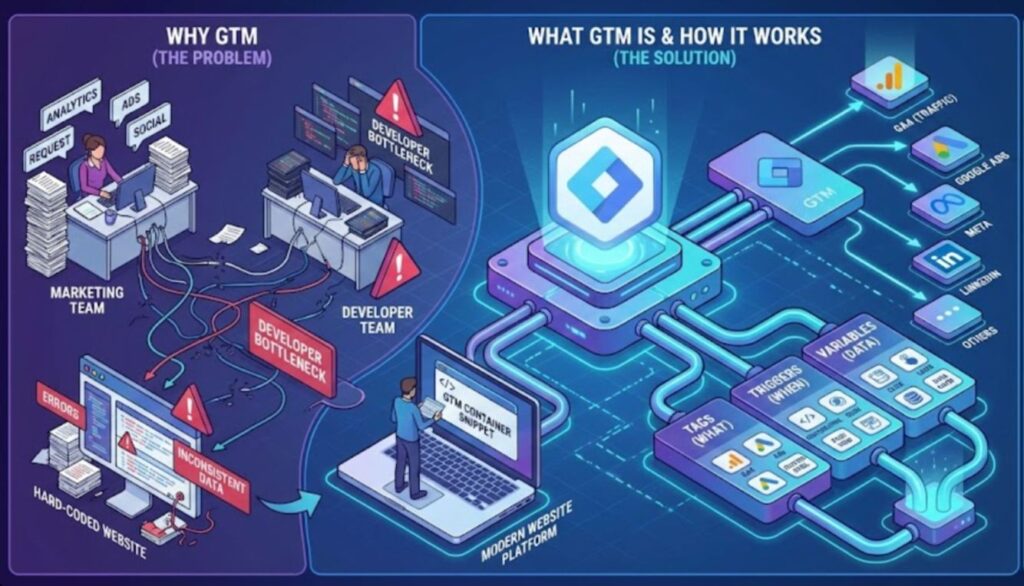
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management system that lets you add, edit, and manage tracking scripts from a single online interface. Instead of placing every script directly into your website’s code, you place one GTM container snippet in the head and another noscript iframe in the body. After that, all tracking is configured inside the GTM interface.
Here is how GTM works:
- Developers place one container code on your website.
- Users manage tracking scripts inside the GTM interface.
- Triggers and conditions decide when each script should run.
GTM does not store data. It simply deploys tags that send information to the platforms you use, such as GA4, Google Ads, Meta, LinkedIn, and others.
Think of GTM as a control center for all your tracking, available without needing a developer for every update.
The Core Elements of GTM
Everything in GTM revolves around three components.
| Component | Explanation | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Tags | These are the scripts or pixels you want to run. Tags send data to platforms like GA4, Google Ads, or Meta. | GA4 Configuration tag, GA4 Event tag (purchase, signup), Google Ads Conversion tag, Remarketing tag, Custom HTML tag. |
| Triggers | Triggers define when your tags should fire. They control the conditions that activate each tag. | Fire GA4 tag on all pages, Fire form submission tag only when a form is submitted, Fire click tracking tag when a specific button is clicked. |
| Variables | Variables store information that tags and triggers use. They capture dynamic data from the page or user actions. | Page URL, Click Text, Data Layer values (ecommerce), Custom JavaScript variables. |
Modern GTM also includes a large template gallery, which reduces the need for custom code and makes implementation more secure and consistent.
Why You Should Use Google Tag Manager
GTM continues to provide major advantages for marketers and developers in 2026.
| Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Speed | No need to wait for development deployments when you want to add or edit tracking scripts. |
| Flexibility | Add, update, or remove tags at any time based on campaign needs. |
| Version Control | Every change creates a version and can be rolled back if something breaks. |
| Built in Debugging | Preview Mode allows you to test tags before publishing to ensure accuracy. |
| Centralized Management | One container snippet supports all tracking needs. |
GTM also supports server-side tagging, which improves data quality, reduces client-side load, and provides better privacy management.
GTM is ideal for any business that wants flexible and reliable tracking without repeatedly involving developers. The platform helps teams work faster and simplifies the implementation of analytics, advertising tags, and custom events.
- Perfect for marketers, analysts, small businesses, and teams with limited engineering support.
- Essential for companies using multiple analytics and advertising platforms that need centralized script management.
Is GTM Still Needed with GA4
GA4 introduced automatic event tracking and a more flexible data model, but it did not replace the need for GTM. Any meaningful customization still requires event configuration, tag deployment, and external platform integrations.
- GTM simplifies advanced GA4 setups such as ecommerce tracking, form submissions, scroll tracking, and button clicks.
- GA4 cannot deploy third party pixels, so GTM remains required for Google Ads, Meta, LinkedIn, TikTok, and other marketing scripts.
Common Beginner Mistakes in GTM Setup
New users often make simple errors that lead to incorrect tracking or slow performance. These mistakes usually come from unclear trigger logic or skipping testing steps.
- Publishing changes without using Preview Mode often leads to broken or duplicated tracking.
- Naming tags, triggers, and variables poorly creates confusion and makes containers harder to maintain over time.
GTM and Privacy Compliance
Privacy regulations like GDPR, PECR, and CCPA require websites to collect data only after users have given consent. GTM does not create compliance automatically, but it works smoothly with consent management platforms and Google Consent Mode.
- It allows conditional tag firing so analytics and marketing scripts load only after the user has opted in.
- Incorrect consent handling can cause data gaps or violations, so every GTM setup needs a clear consent strategy.
How GTM Fits Into a Modern Analytics Stack
GTM functions as the operational layer for data collection in 2026. It connects websites to analytics tools, ad platforms, and backend systems while supporting complex data needs.
- GTM sends structured events into GA4, Google Ads, Meta, LinkedIn, BigQuery, and automation workflows.
- When combined with server-side tagging, GTM improves data accuracy, reduces page load, and strengthens privacy and governance.