Most SaaS and digital-first companies reach a point where growth becomes harder to explain than to execute. Traffic increases. Campaigns scale. Product velocity improves. Yet leadership teams still struggle to answer basic questions with confidence:
- Where are our best customers really coming from?
- What actions actually lead users to conversion?
- Why do users drop off before realizing value?
When these questions surface repeatedly, the issue is rarely a lack of data. It is a lack of clarity. This is the problem Google Analytics 4 was created to solve.
This guide is a pillar-level explanation of how Google Analytics works, written specifically for founders, marketers, and product leaders who need clarity, not dashboards for their own sake. It explains the system from first principles, shows how the Google analytics stack fits together, and helps you turn user behavior into decisions that drive growth.
What Google Analytics Is Actually Designed to Do
Google Analytics exists to help businesses understand how people behave when they interact with websites and applications. It does not start by telling you what to measure. Instead, it observes real user actions and structures those actions into data that can be analyzed over time. The purpose is insight, not reporting.
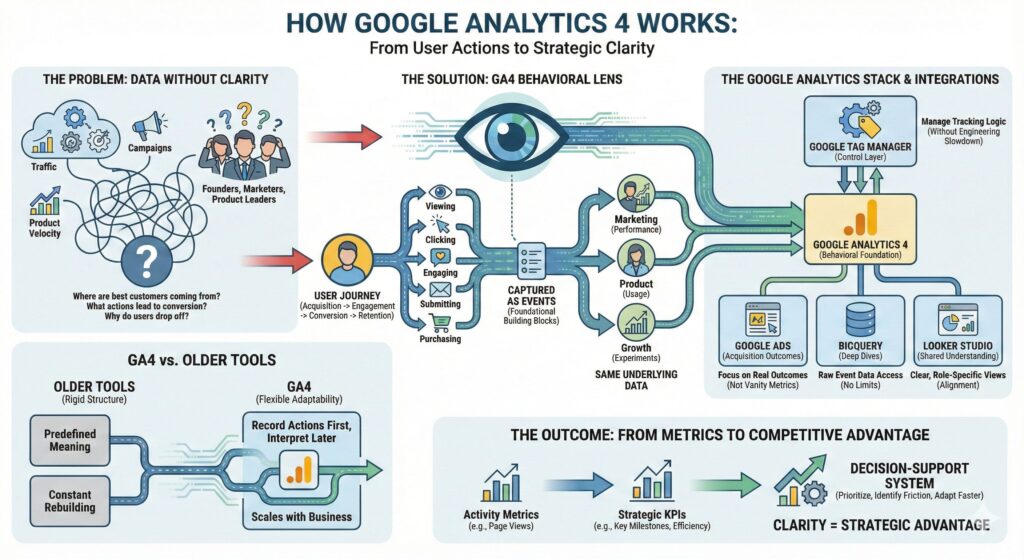
For leadership teams, this distinction matters. Reporting answers what happened. Analytics answers why it happened and what to do next.
Google Analytics provides a behavioral lens across the entire user journey, from acquisition to engagement to conversion and retention.
How Google Analytics Collects User Behavior
Understanding how Google Analytics works starts with understanding how behavior is captured. Every meaningful user action leaves a signal, including:
- Viewing a page or screen
- Clicking a button or link
- Engaging with a feature
- Submitting a form
- Completing a purchase
In Google Analytics, these actions are recorded as events. Events are the foundational building blocks of the platform.
Individually, events may seem insignificant. Together, they reveal patterns that show how users discover products, evaluate value, encounter friction, and decide whether to convert or leave. This event-based model allows teams to analyze marketing performance, product usage, and growth experiments using the same underlying data.
The Reality of Modern Tracking Challenges
Accurate tracking is far more complex than most organizations expect. Teams face challenges such as:
- Users switching devices and browsers
- Privacy regulations restricting data collection
- Consent requirements varying by region
- Browser limitations on cookies
- Multiple tools reporting conflicting metrics
When advertising platforms, product dashboards, and revenue systems disagree, trust in data erodes. Analytics becomes something teams debate rather than rely on.
Google Analytics does not eliminate these challenges, but it creates a single behavioral foundation teams can align around.
Why Google Tag Manager Is Critical
The quality of your analytics depends heavily on how it is implemented. This is where Google Tag Manager becomes essential. Google Tag Manager acts as a control layer between your website or application and your analytics tools. Instead of hard-coding tracking logic into the site, teams define:
- What actions to track
- When data should be sent
- Under which conditions tracking should fire
The value of Google Tag Manager is operational, not technical.
It allows analytics to evolve without slowing engineering teams, makes tracking logic easier to audit, and reduces the risk of broken or inconsistent measurement.
Connecting Acquisition to Outcomes with Google Ads
Analytics becomes significantly more valuable when tied to acquisition data. By integrating Google Analytics with Google Ads, teams move beyond vanity metrics and focus on real outcomes. Instead of asking which campaigns drove the most clicks, leaders can understand:
- Which campaigns bring engaged users
- Which sources drive conversions
- Which channels create long-term value
This shifts marketing conversations from activity to impact and supports smarter budget allocation.
Going Deeper with BigQuery
As organizations scale, their questions outgrow standard dashboards. Teams want to understand how behavior changes over time, how features influence conversion, and how long it takes users to reach meaningful milestones. This is where BigQuery becomes essential.
BigQuery provides access to the raw event-level data collected by Google Analytics. Analysts can explore behavior without predefined limits. For decision makers, this transparency builds trust. Metrics can be explained, validated, and challenged logically rather than accepted as black boxes.
Turning Data into Shared Understanding with Looker Studio
Insight only creates value when it is shared and understood. Looker Studio translates analytics data into clear, role-specific views across the organization.
Executives monitor strategic trends. Marketing teams evaluate performance. Product teams analyze engagement and adoption. When everyone uses the same underlying data foundation, alignment improves and decision-making accelerates.
From Metrics to KPIs That Actually Matter
One of the most important shifts Google Analytics enables is the move from metrics to KPIs. Metrics measure activity. KPIs measure progress toward business goals.
Page views, sessions, and clicks rarely drive meaningful decisions on their own. What matters is understanding how many users reach key milestones, how efficiently they convert, and how behavior evolves across the lifecycle.
Google Analytics provides the foundation to define success in terms that actually matter to the business.
What Google Analytics Does Not Do
It is just as important to understand the limits of Google Analytics.
It is not a CRM, not a customer support platform, and not a substitute for business strategy.
It does not automatically fix poor data quality or make decisions on behalf of leadership. Its value depends on thoughtful implementation, clear goals, and disciplined interpretation.
Why Google Analytics Is a Competitive Advantage
For SaaS and digital-first businesses, understanding user behavior is no longer optional.
Companies that can clearly see how users interact with their digital experiences are better equipped to prioritize investments, identify friction early, and adapt faster to change.
When Google Analytics, Google Tag Manager, Google Ads, BigQuery, and Looker Studio are used together, they form a modern analytics foundation that replaces guesswork with clarity.
How Google Analytics Works in Practice
Google Analytics works by observing real user behavior, structuring it into events, and enabling teams to analyze those events across marketing, product, and growth use cases.
When implemented correctly and connected to the broader Google analytics stack, it becomes a decision-support system rather than a reporting tool.
For founders, marketers, and product leaders, this clarity is not just useful. It is a strategic advantage.
